Difference between revisions of "Model Customization"
m |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div id="mw-content-text" lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"><table style="color: white; background-color: steelblue;" cellpadding="10" width="100%"> | <div id="mw-content-text" lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"><table style="color: white; background-color: steelblue;" cellpadding="10" width="100%"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td colspan="1"> [[File:Dialog-warning.png | + | <td colspan="1"> [[File:Dialog-warning.png|32px]] This tutorial requires advanced Python programming skills. |
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
<h2>Introduction</h2> | <h2>Introduction</h2> | ||
<p>You can override various internal model calculation routines with custom python code using the <b>Script Manager</b>. As of <b>DWSIM v5.6 Update 12</b>, you can override calculation routines from Unit Operations on the flowsheet, Fugacity, Enthalpy and Entropy calculation routines from Property Packages added to the flowsheet and use custom Flash calculation routines through User-Defined Flash Algorithm instances added to the flowsheet. | <p>You can override various internal model calculation routines with custom python code using the <b>Script Manager</b>. As of <b>DWSIM v5.6 Update 12</b>, you can override calculation routines from Unit Operations on the flowsheet, Fugacity, Enthalpy and Entropy calculation routines from Property Packages added to the flowsheet and use custom Flash calculation routines through User-Defined Flash Algorithm instances added to the flowsheet. | ||
</p><p>The custom functions must be defined and set only once before working with your simulation. For this reason it is better to associate your code with the <b>Simulation Opened</b> event after it is ready for production, so it can be automatically executed on every simulation file opening/loading. | </p><p>The custom functions must be defined and set only once before working with your simulation. For this reason it is better to associate your code with the <b>Simulation Opened</b> event after it is ready for production, so it can be automatically executed on every simulation file opening/loading. | ||
| − | |||
</p><p>If you choose to make any modifications to the code, don't forget to update it by running the script using the 'Run Script' button on the Script Manager. | </p><p>If you choose to make any modifications to the code, don't forget to update it by running the script using the 'Run Script' button on the Script Manager. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<h3>Unit Operations</h3> | <h3>Unit Operations</h3> | ||
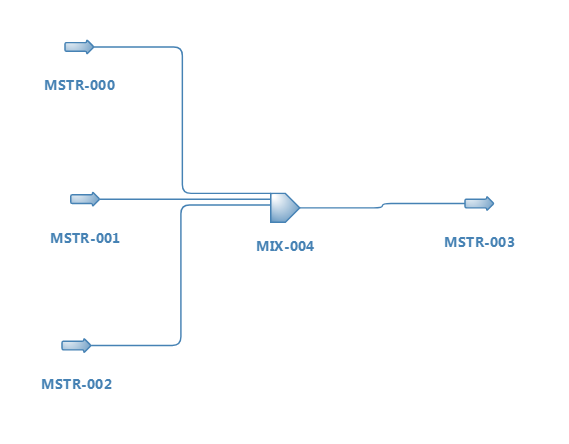
<p>The following example shows how to override the calculation routine of a simple mixer. The Python code is a direct conversion from DWSIM's Mixer calculation routine, just for illustration purposes. It works with this sample flowsheet: | <p>The following example shows how to override the calculation routine of a simple mixer. The Python code is a direct conversion from DWSIM's Mixer calculation routine, just for illustration purposes. It works with this sample flowsheet: | ||
| − | </p><p> | + | </p><p>[[File:Mixer.png]] |
</p><p>First, you must define a Python function which takes no arguments and does the calculation and sets properties of outlet material streams. This function doesn't need to return anything. Then you set the <b>OverrideCalculationRoutine</b> to true and the <b>CalculationRoutineOverride</b> property to your function's delegate (= name). | </p><p>First, you must define a Python function which takes no arguments and does the calculation and sets properties of outlet material streams. This function doesn't need to return anything. Then you set the <b>OverrideCalculationRoutine</b> to true and the <b>CalculationRoutineOverride</b> property to your function's delegate (= name). | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
import clr | import clr | ||
| Line 132: | Line 133: | ||
mixer.CalculationRoutineOverride = CalcMixer | mixer.CalculationRoutineOverride = CalcMixer | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| − | <p>After updating the script and running the simulation, you should get the following output: | + | |
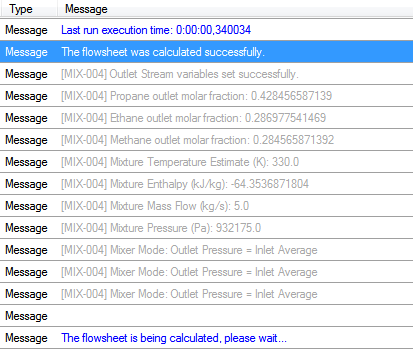
| − | [[File:Mixer_out.png]] | + | <p>After updating the script and running the simulation, you should get the following output:</p> |
| + | <p>[[File:Mixer_out.png]] | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<h3>Material Streams</h3> | <h3>Material Streams</h3> | ||
| Line 143: | Line 145: | ||
<p>The following code overrides the fugacity coefficient calculation routines (called by the K-values calculation routine which is, by its turn, called by the flash algorithms to do the equilibrium calculations) from a Peng-Robinson Property Package instance added to the simulation. The code reproduces the internal DWSIM's PR routines, just for illustration purposes. | <p>The following code overrides the fugacity coefficient calculation routines (called by the K-values calculation routine which is, by its turn, called by the flash algorithms to do the equilibrium calculations) from a Peng-Robinson Property Package instance added to the simulation. The code reproduces the internal DWSIM's PR routines, just for illustration purposes. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
import clr | import clr | ||
| Line 313: | Line 316: | ||
pp.KvalFugacityCoefficientOverride = fugcoeff | pp.KvalFugacityCoefficientOverride = fugcoeff | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | |||
<h3>Enthalpy/Entropy</h3> | <h3>Enthalpy/Entropy</h3> | ||
<p>The following code overrides the enthalpy calculation routine (called by the Material Stream's Phase Property and by Pressure-Enthalpy flash routines) from a Peng-Robinson Property Package instance added to the simulation. The code reproduces the internal DWSIM's PR routines, just for illustration purposes. | <p>The following code overrides the enthalpy calculation routine (called by the Material Stream's Phase Property and by Pressure-Enthalpy flash routines) from a Peng-Robinson Property Package instance added to the simulation. The code reproduces the internal DWSIM's PR routines, just for illustration purposes. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
import clr | import clr | ||
| Line 500: | Line 505: | ||
pp.EnthalpyCalculationOverride = enthalpy | pp.EnthalpyCalculationOverride = enthalpy | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | |||
<p>The Entropy override works the same way by defining the <b>OverrideEntropyCalculation/EntropyCalculationOverride</b> properties from the Property Package instance. | <p>The Entropy override works the same way by defining the <b>OverrideEntropyCalculation/EntropyCalculationOverride</b> properties from the Property Package instance. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 512: | Line 518: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<h3>PT Flash</h3> | <h3>PT Flash</h3> | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
import clr | import clr | ||
| Line 726: | Line 734: | ||
udflash.PTFlash = PTFlash | udflash.PTFlash = PTFlash | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
<h3>PH/PS Flash</h3> | <h3>PH/PS Flash</h3> | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
import clr | import clr | ||
| Line 1,046: | Line 1,055: | ||
udflash.PSFlash = PSFlash | udflash.PSFlash = PSFlash | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
<h3>PVF/TVF Flash</h3> | <h3>PVF/TVF Flash</h3> | ||
<p>Usually you don't need to set/define a function to Pressure-VaporFraction and/or Temperature-VaporFraction Flashes unless you're working with one or more of the following: | <p>Usually you don't need to set/define a function to Pressure-VaporFraction and/or Temperature-VaporFraction Flashes unless you're working with one or more of the following: | ||
| Line 1,058: | Line 1,067: | ||
<li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/samples/User-Defined%20Flash.dwxmz User-Defined Flash.dwxmz]</li></ul> | <li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/samples/User-Defined%20Flash.dwxmz User-Defined Flash.dwxmz]</li></ul> | ||
<h2>More Information</h2> | <h2>More Information</h2> | ||
| − | <ul><li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/ | + | <ul><li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/api_help60/index.html API Documentation for DWSIM v6.x]</li> |
| − | <li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/ | + | <li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/api_help60/html/T_DWSIM_Thermodynamics_PropertyPackages_State.htm State Enumeration]</li> |
| − | <li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/ | + | <li> [http://dwsim.inforside.com.br/api_help60/html/T_DWSIM_Thermodynamics_PropertyPackages_Auxiliary_FlashAlgorithms_FlashCalculationResult.htm FlashCalculationResult class]</li> |
<li> [http://ironpython.net/documentation/ IronPython Documentation]<br /></li> | <li> [http://ironpython.net/documentation/ IronPython Documentation]<br /></li> | ||
<li> [http://www.ironpython.info/index.php/Using_the_Python_Standard_Library Using the Python Standard Library]<br /></li> | <li> [http://www.ironpython.info/index.php/Using_the_Python_Standard_Library Using the Python Standard Library]<br /></li> | ||
<li> [http://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide Python for Beginners]<br /></li></ul></div> | <li> [http://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide Python for Beginners]<br /></li></ul></div> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:33, 10 March 2021
| |
| |
Contents
Introduction
You can override various internal model calculation routines with custom python code using the Script Manager. As of DWSIM v5.6 Update 12, you can override calculation routines from Unit Operations on the flowsheet, Fugacity, Enthalpy and Entropy calculation routines from Property Packages added to the flowsheet and use custom Flash calculation routines through User-Defined Flash Algorithm instances added to the flowsheet.
The custom functions must be defined and set only once before working with your simulation. For this reason it is better to associate your code with the Simulation Opened event after it is ready for production, so it can be automatically executed on every simulation file opening/loading.
If you choose to make any modifications to the code, don't forget to update it by running the script using the 'Run Script' button on the Script Manager.
Unit Operation / Material Stream Calculation Routine Override
Unit Operations
The following example shows how to override the calculation routine of a simple mixer. The Python code is a direct conversion from DWSIM's Mixer calculation routine, just for illustration purposes. It works with this sample flowsheet:
First, you must define a Python function which takes no arguments and does the calculation and sets properties of outlet material streams. This function doesn't need to return anything. Then you set the OverrideCalculationRoutine to true and the CalculationRoutineOverride property to your function's delegate (= name).
import clr
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.MathOps')
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.UnitOperations')
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.Interfaces')
from DWSIM import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.Streams import *
from DWSIM.UnitOperations import *
from DWSIM.MathOps.MathEx import *
from System import *
from System.Collections.Generic import *
# gets the mixer object
mixer = Flowsheet.GetFlowsheetSimulationObject('MIX-004')
def CalcMixer():
ms = MaterialStream()
P = 0.0
W = 0.0
H = 0.0
i = 0
for cp in mixer.GraphicObject.InputConnectors:
if cp.IsAttached:
ms = Flowsheet.SimulationObjects[cp.AttachedConnector.AttachedFrom.Name]
ms.Validate()
if mixer.PressureCalculation == UnitOperations.Mixer.PressureBehavior.Minimum:
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixer Mode: Outlet Pressure = Minimum Inlet Pressure'
if ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure < P:
P = ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure
elif P == 0.0:
P = ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure
elif mixer.PressureCalculation == UnitOperations.Mixer.PressureBehavior.Maximum:
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixer Mode: Outlet Pressure = Maximum Inlet Pressure'
if ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure > P:
P = ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure
elif P == 0:
P = ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure
else:
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixer Mode: Outlet Pressure = Inlet Average'
P += ms.Phases[0].Properties.pressure
i += 1
We = ms.Phases[0].Properties.massflow
W += We
if not Double.IsNaN(ms.Phases[0].Properties.enthalpy): H += We * ms.Phases[0].Properties.enthalpy
if W != 0.0:
Hs = H / W
else:
Hs = 0.0
if mixer.PressureCalculation == UnitOperations.Mixer.PressureBehavior.Average: P = P / (i - 1)
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixture Pressure (Pa): ' + str(P)
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixture Mass Flow (kg/s): ' + str(W)
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixture Enthalpy (kJ/kg): ' + str(Hs)
T = 0.0
n = Flowsheet.SelectedCompounds.Count
Vw = Dictionary[String, Double]()
for cp in mixer.GraphicObject.InputConnectors:
if cp.IsAttached:
ms = Flowsheet.SimulationObjects[cp.AttachedConnector.AttachedFrom.Name]
for comp in ms.Phases[0].Compounds.Values:
if not Vw.ContainsKey(comp.Name):
Vw.Add(comp.Name, 0)
Vw[comp.Name] += comp.MassFraction * ms.Phases[0].Properties.massflow
if W != 0.0: T += ms.Phases[0].Properties.massflow / W * ms.Phases[0].Properties.temperature
if W == 0.0: T = 273.15
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Mixture Temperature Estimate (K): ' + str(T)
omstr = Flowsheet.SimulationObjects[mixer.GraphicObject.OutputConnectors[0].AttachedConnector.AttachedTo.Name]
omstr.Clear()
omstr.ClearAllProps()
if W != 0.0: omstr.Phases[0].Properties.enthalpy = Hs
omstr.Phases[0].Properties.pressure = P
omstr.Phases[0].Properties.massflow = W
omstr.Phases[0].Properties.molarfraction = 1
omstr.Phases[0].Properties.massfraction = 1
for comp in omstr.Phases[0].Compounds.Values:
if W != 0.0: comp.MassFraction = Vw[comp.Name] / W
mass_div_mm = 0.0
for sub1 in omstr.Phases[0].Compounds.Values:
mass_div_mm += sub1.MassFraction / sub1.ConstantProperties.Molar_Weight
for sub1 in omstr.Phases[0].Compounds.Values:
if W != 0.0:
sub1.MoleFraction = sub1.MassFraction / sub1.ConstantProperties.Molar_Weight / mass_div_mm
else:
sub1.MoleFraction = 0.0
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + sub1.Name + ' outlet molar fraction: ' + str(sub1.MoleFraction)
omstr.Phases[0].Properties.temperature = T
omstr.SpecType = Interfaces.Enums.StreamSpec.Pressure_and_Enthalpy
print '[' + mixer.GraphicObject.Tag + '] ' + 'Outlet Stream variables set successfully.'
return None
mixer.OverrideCalculationRoutine = True
mixer.CalculationRoutineOverride = CalcMixer
After updating the script and running the simulation, you should get the following output:
Material Streams
Usually you don't need to override the calculation routines of material streams as they are very structured and involve a lot of internal checks and property updates.
Property Package Fugacity Coefficients / Enthalpy / Entropy Calculation Routine Override
Fugacity Coefficients
The following code overrides the fugacity coefficient calculation routines (called by the K-values calculation routine which is, by its turn, called by the flash algorithms to do the equilibrium calculations) from a Peng-Robinson Property Package instance added to the simulation. The code reproduces the internal DWSIM's PR routines, just for illustration purposes.
import clr
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.MathOps')
from DWSIM import *
from DWSIM.MathOps.MathEx import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.PropertyPackages import *
from System import *
# gets the first Property Package added to the the simulation
pp = Flowsheet.PropertyPackagesArray[0]
def calcroots(coeffs):
# auxiliary function
# calculates the roots of of a cubic polynomial and returns only the real ones
a = coeffs[0]
b = coeffs[1]
c = coeffs[2]
d = coeffs[3]
# uses DWSIM's internal 'CalcRoots' function to calculate roots
# https://github.com/DanWBR/dwsim5/blob/windows/DWSIM.Math/MATRIX2.vb#L29
res = PolySolve.CalcRoots(a, b, c, d)
roots = [[0] * 2 for i in range(3)]
roots[0][0] = res[0, 0]
roots[0][1] = res[0, 1]
roots[1][0] = res[1, 0]
roots[1][1] = res[1, 1]
roots[2][0] = res[2, 0]
roots[2][1] = res[2, 1]
# orders the roots
if roots[0][0] > roots[1][0]:
tv = roots[1][0]
roots[1][0] = roots[0][0]
roots[0][0] = tv
tv2 = roots[1][1]
roots[1][1] = roots[0][1]
roots[0][1] = tv2
if roots[0][0] > roots[2][0]:
tv = roots[2][0]
roots[2][0] = roots[0][0]
roots[0][0] = tv
tv2 = roots[2][1]
roots[2][1] = roots[0][1]
roots[0][1] = tv2
if roots[1][0] > roots[2][0]:
tv = roots[2][0]
roots[2][0] = roots[1][0]
roots[1][0] = tv
tv2 = roots[2][1]
roots[2][1] = roots[1][1]
roots[1][1] = tv2
validroots = []
if roots[0][1] == 0 and roots[0][0] > 0.0: validroots.append(roots[0][0])
if roots[1][1] == 0 and roots[1][0] > 0.0: validroots.append(roots[1][0])
if roots[2][1] == 0 and roots[2][0] > 0.0: validroots.append(roots[2][0])
# returns only valid real roots
return validroots
def fugcoeff(Vz, T, P, state):
# calculates fugacity coefficients using PR EOS
# Vx = composition vector in molar fractions
# T = temperature in K
# P = Pressure in Pa
# state = mixture state (Liquid, Vapor or Solid)
R = 8.314
n = len(Vz)
Tc = pp.RET_VTC() # critical temperatures
Pc = pp.RET_VPC() # critical pressures
w = pp.RET_VW() # acentric factors
alpha = [0] * n
ai = [0] * n
bi = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
alpha[i] = (1 + (0.37464 + 1.54226 * w[i] - 0.26992 * w[i] ** 2) * (1 - (T / Tc[i]) ** 0.5)) ** 2
ai[i] = 0.45724 * alpha[i] * R ** 2 * Tc[i] ** 2 / Pc[i]
bi[i] = 0.0778 * R * Tc[i] / Pc[i]
a = [[0] * n for i in range(n)]
# get binary interaction parameters (BIPs/kijs) from PR Property Package
kij = [[0] * n for i in range(n)]
vkij = pp.RET_VKij()
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
kij[i][j] = vkij[i, j]
a[i][j] = (ai[i] * ai[j]) ** 0.5 * (1 - kij[i][j]) # <- default mixing rule for amix
amix = 0.0
bmix = 0.0
amix2 = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
amix += Vz[i] * Vz[j] * a[i][j] # <- default mixing rule for amix
amix2[i] += Vz[j] * a[j][i]
for i in range(n):
bmix += Vz[i] * bi[i] # <- default mixing rule - no interaction parameters for bmix
AG = amix * P / (R * T) ** 2
BG = bmix * P / (R * T)
coeff = [0] * 4
coeff[0] = 1
coeff[1] = BG - 1
coeff[2] = AG - 3 * BG ** 2 - 2 * BG
coeff[3] = -AG * BG + BG ** 2 + BG ** 3
roots = calcroots(coeff) # <- get the real roots of the cubic equation
# compressibility factor = cubic equation's root
if state == State.Liquid:
# liquid
Z = min(roots)
else:
# vapor
Z = max(roots)
# gets a special zeroed vector from the property package because DWSIM requires a
# .NET array as the returning value, not a Python one
fugcoeff = pp.RET_NullVector()
for i in range(n):
t1 = bi[i] * (Z - 1) / bmix
t2 = -Math.Log(Z - BG)
t3 = AG * (2 * amix2[i] / amix - bi[i] / bmix)
t4 = Math.Log((Z + (1 + 2 ** 0.5) * BG) / (Z + (1 - 2 ** 0.5) * BG))
t5 = 2 * 2 ** 0.5 * BG
fugcoeff[i] = Math.Exp(t1 + t2 - (t3 * t4 / t5))
# returns calculated fugacity coefficients
print 'calculated fugacities = ' + str(fugcoeff) + ' (' + str(state) + ')'
return fugcoeff
# activate fugacity calculation override on PR Property Package
pp.OverrideKvalFugCoeff = True
# set the function that calculates the fugacity coefficient
pp.KvalFugacityCoefficientOverride = fugcoeff
Enthalpy/Entropy
The following code overrides the enthalpy calculation routine (called by the Material Stream's Phase Property and by Pressure-Enthalpy flash routines) from a Peng-Robinson Property Package instance added to the simulation. The code reproduces the internal DWSIM's PR routines, just for illustration purposes.
import clr
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.MathOps')
from DWSIM import *
from DWSIM.MathOps.MathEx import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.PropertyPackages import *
from System import *
# gets the first Property Package added to the the simulation
pp = Flowsheet.PropertyPackagesArray[0]
def calcroots(coeffs):
# auxiliary function
# calculates the roots of of a cubic polynomial and returns only the real ones
a = coeffs[0]
b = coeffs[1]
c = coeffs[2]
d = coeffs[3]
# uses DWSIM's internal 'CalcRoots' function to calculate roots
# https://github.com/DanWBR/dwsim5/blob/windows/DWSIM.Math/MATRIX2.vb#L29
res = PolySolve.CalcRoots(a, b, c, d)
roots = [[0] * 2 for i in range(3)]
roots[0][0] = res[0, 0]
roots[0][1] = res[0, 1]
roots[1][0] = res[1, 0]
roots[1][1] = res[1, 1]
roots[2][0] = res[2, 0]
roots[2][1] = res[2, 1]
# orders the roots
if roots[0][0] > roots[1][0]:
tv = roots[1][0]
roots[1][0] = roots[0][0]
roots[0][0] = tv
tv2 = roots[1][1]
roots[1][1] = roots[0][1]
roots[0][1] = tv2
if roots[0][0] > roots[2][0]:
tv = roots[2][0]
roots[2][0] = roots[0][0]
roots[0][0] = tv
tv2 = roots[2][1]
roots[2][1] = roots[0][1]
roots[0][1] = tv2
if roots[1][0] > roots[2][0]:
tv = roots[2][0]
roots[2][0] = roots[1][0]
roots[1][0] = tv
tv2 = roots[2][1]
roots[2][1] = roots[1][1]
roots[1][1] = tv2
validroots = []
if roots[0][1] == 0 and roots[0][0] > 0.0: validroots.append(roots[0][0])
if roots[1][1] == 0 and roots[1][0] > 0.0: validroots.append(roots[1][0])
if roots[2][1] == 0 and roots[2][0] > 0.0: validroots.append(roots[2][0])
# returns only valid real roots
return validroots
def enthalpy(Vz, T, P, state):
# calculates enthalpy using PR EOS
# Vx = composition vector in molar fractions
# T = temperature in K
# P = Pressure in Pa
# state = mixture state (Liquid, Vapor or Solid)
# ideal gas enthalpy contribution
Hid = pp.RET_Hid(298.15, T, Vz)
R = 8.314
n = len(Vz)
Tc = pp.RET_VTC() # critical temperatures
Pc = pp.RET_VPC() # critical pressures
w = pp.RET_VW() # acentric factors
alpha = [0] * n
ai = [0] * n
bi = [0] * n
ci = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
alpha[i] = (1 + (0.37464 + 1.54226 * w[i] - 0.26992 * w[i] ** 2) * (1 - (T / Tc[i]) ** 0.5)) ** 2
ai[i] = 0.45724 * alpha[i] * R ** 2 * Tc[i] ** 2 / Pc[i]
bi[i] = 0.0778 * R * Tc[i] / Pc[i]
ci[i] = 0.37464 + 1.54226 * w[i] - 0.26992 * w[i] ** 2
a = [[0] * n for i in range(n)]
# get binary interaction parameters (BIPs/kijs) from PR Property Package
kij = [[0] * n for i in range(n)]
vkij = pp.RET_VKij()
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
kij[i][j] = vkij[i, j]
a[i][j] = (ai[i] * ai[j]) ** 0.5 * (1 - kij[i][j]) # <- default mixing rule for amix
amix = 0.0
bmix = 0.0
amix2 = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
amix += Vz[i] * Vz[j] * a[i][j] # <- default mixing rule for amix
amix2[i] += Vz[j] * a[j][i]
for i in range(n):
bmix += Vz[i] * bi[i] # <- default mixing rule - no interaction parameters for bmix
AG = amix * P / (R * T) ** 2
BG = bmix * P / (R * T)
coeff = [0] * 4
coeff[0] = 1
coeff[1] = BG - 1
coeff[2] = AG - 3 * BG ** 2 - 2 * BG
coeff[3] = -AG * BG + BG ** 2 + BG ** 3
roots = calcroots(coeff) # <- get the real roots of the cubic equation
# compressibility factor = cubic equation's root
if state == State.Liquid:
# liquid
Z = min(roots)
else:
# vapor
Z = max(roots)
# amix temperature derivative
dadT1 = -8.314 / 2 * (0.45724 / T) ** 0.5
dadT2 = 0.0#
for i in range(n):
j = 0
for j in range(n):
dadT2 += Vz[i] * Vz[j] * (1 - kij[i][j]) * (ci[j] * (ai[i] * Tc[j] / Pc[j]) ** 0.5 + ci[i] * (ai[j] * Tc[i] / Pc[i]) ** 0.5)
dadT = dadT1 * dadT2
uu = 2
ww = -1
DAres = amix / (bmix * (uu ** 2 - 4 * ww) ** 0.5) * Math.Log((2 * Z + BG * (uu - (uu ** 2 - 4 * ww) ** 0.5)) / (2 * Z + BG * (uu + (uu ** 2 - 4 * ww) ** 0.5))) - R * T * Math.Log((Z - BG) / Z) - R * T * Math.Log(Z)
DSres = R * Math.Log((Z - BG) / Z) + R * Math.Log(Z) - 1 / (8 ** 0.5 * bmix) * dadT * Math.Log((2 * Z + BG * (2 - 8 ** 0.5)) / (2 * Z + BG * (2 + 8 ** 0.5)))
DHres = DAres + T * (DSres) + R * T * (Z - 1)
# mixture molar weight (MW)
MW = pp.AUX_MMM(Vz)
print 'calculated enthalpy = ' + str(Hid + DHres/ MW) + ' kJ/kg (' + str(state) + ')'
return Hid + DHres / MW # kJ/kg
# activate enthalpy calculation override on PR Property Package
pp.OverrideEnthalpyCalculation = True
# set the function that calculates the enthalpy
pp.EnthalpyCalculationOverride = enthalpy
The Entropy override works the same way by defining the OverrideEntropyCalculation/EntropyCalculationOverride properties from the Property Package instance.
User-Defined Flash Algorithm Routines
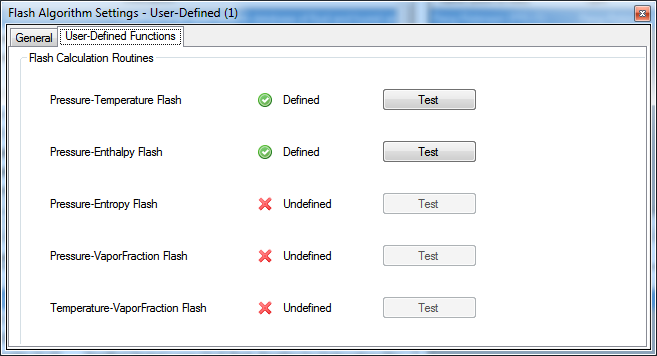
DWSIM v5.6 Update 12 includes a new Flash Algorithm type, the User-Defined (Python) Flash Algorithm. With this flash type you can define custom python functions to calculate the Pressure/Temperature, Pressure/Enthalpy, Pressure/Entropy, Pressure/VaporFraction and Temperature/VaporFraction flashes.
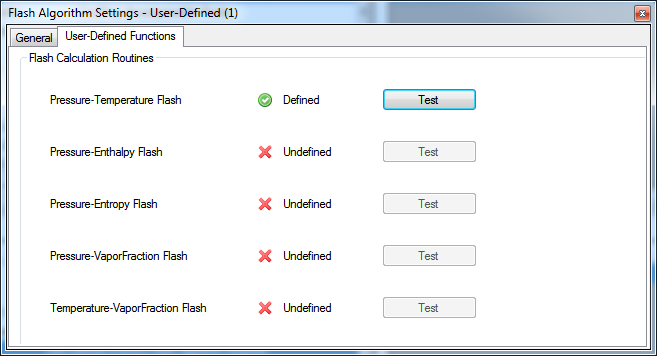
As you define the flash algorithm delegates through the Script Manager, the Flash Algorithm configuration editor displays the current status of the defined routines. You can test them using the corresponding buttons on the editor.
The following code sample reproduces the PT/PH/PS flash routines from DWSIM's Nested Loops VLE flash algorithm, for illustration purposes. More advanced calculations can be implemented by the user.
PT Flash
import clr
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.MathOps')
from DWSIM import *
from DWSIM.MathOps.MathEx import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.PropertyPackages import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.PropertyPackages.Auxiliary.FlashAlgorithms import *
from System import *
from System.Collections.Generic import *
# gets the first Flash Algorithm (= User-Defined) added to the simulation
udflash = Flowsheet.FlowsheetOptions.FlashAlgorithms[0]
def PTFlash(Vz, P, T, pp):
n = len(Vz)
L = 0.0
V = 0.0
Vy = [0] * n
Vx = [0] * n
Ki = [0] * n
Vp = [0] * n
count = 0
alreadysolved = False
if T > Common.Max(pp.RET_VTC(), Array[Double](Vz)):
# supercritical mixture
alreadysolved = True
Vy = list(Vz)
Vx = list(Vz)
V = 1.0
L = 0.0
for i in range(n):
Vp[i] = pp.AUX_PVAPi(i, T)
Ki[i] = Vp[i] / P
Px = 0.0
for i in range(n):
if Vp[i] != 0.0: Px += Vz[i] / Vp[i]
Px = 1 / Px
Pmin = Px
Px = 0.0
for i in range(n):
Px += Vz[i] * Vp[i]
Pmax = Px
Pb = Pmax
Pd = Pmin
if Math.Abs(Pb - Pd) / Pb < 0.0000001:
# one comp only
alreadysolved = True
Px = sum(Vp * Vz)
if Px <= P:
L = 1.0
V = 0.0
Vx = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Vx[i] * Ki[i]
else:
L = 0.0
V = 1.0
Vy = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
if alreadysolved == False:
Vmin = 1.0#
Vmax = 0.0#
for i in range(n):
if (Ki[i] * Vz[i] - 1) / (Ki[i] - 1) < Vmin: Vmin = (Ki[i] * Vz[i] - 1) / (Ki[i] - 1)
if (1 - Vz[i]) / (1 - Ki[i]) > Vmax: Vmax = (1 - Vz[i]) / (1 - Ki[i])
if Vmin < 0.0: Vmin = 0.0
if Vmin == 1.0: Vmin = 0.0
if Vmax == 0.0: Vmax = 1.0
if Vmax > 1.0: Vmax = 1.0
V = (Vmin + Vmax) / 2
g = 0.0
for i in range(n):
g += Vz[i] * (Ki[i] - 1) / (V + (1 - V) * Ki[i])
if g > 0.0:
Vmin = V
else:
Vmax = V
V = Vmin + (Vmax - Vmin) / 2
L = 1.0 - V
for i in range(n):
if Vz[i] != 0.0:
Vy[i] = Vz[i] * Ki[i] / ((Ki[i] - 1) * V + 1)
if Ki[i] != 0.0:
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
else:
Vx[i] = Vz[i]
if Vy[i] < 0.0: Vy[i] = 0.0
if Vx[i] < 0.0: Vx[i] = 0.0
else:
Vy[i] = 0.0
Vx[i] = 0.0
error = 1E10
Vy_prev = [0] * n
Vx_prev = [0] * n
Ki_prev = [0] * n
V_ant = V
while error > 1E-6:
Ki_prev = list(Ki)
Ki = pp.DW_CalcKvalue(Array[Double](Vx), Array[Double](Vy), T, P)
Vy_prev = list(Vy)
Vx_prev = list(Vx)
if V == 1.0:
Vy = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
elif V == 0.0:
Vx = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Ki[i] * Vx[i]
else:
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Vz[i] * Ki[i] / ((Ki[i] - 1) * V + 1)
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
error = 0.0
for i in range(n):
error += Math.Abs(Vx[i] - Vx_prev[i]) + Math.Abs(Vy[i] - Vy_prev[i])
V_prev = V
F = 0.0
dF = 0.0
for i in range(n):
if Vz[i] > 0.0:
F += Vz[i] * (Ki[i] - 1) / (1 + V * (Ki[i] - 1))
dF -= Vz[i] * (Ki[i] - 1) ** 2 / (1 + V * (Ki[i] - 1)) ** 2
if Math.Abs(F) < 1E-6: break
V = -F / dF + V_prev
L = 1.0 - V
if V <= 0.0:
V = 0.0
L = 1.0
Vx = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Ki[i] * Vx[i]
if V >= 1.0:
V = 1.0
L = 0.0
Vy = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
if Math.Abs(V - V_prev) < 1E-6: break
count += 1
if count > 100: raise Exception("PT Flash: Maximum Iterations Reached")
print 'PT Flash iteration #' + str(count) + ' (V = ' + str(V) + ', convergence error = ' + str(error) + ')'
Vyn = [0] * n
Vxn = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
Vyn[i] = V * Vy[i]
Vxn[i] = L * Vx[i]
results = FlashCalculationResult(pp.DW_GetConstantProperties())
results.MixtureMoleAmounts = List[Double](Vz)
zerovec = pp.RET_NullVector()
results.VaporPhaseMoleAmounts = List[Double](Vyn)
results.LiquidPhase1MoleAmounts = List[Double](Vxn)
results.LiquidPhase2MoleAmounts = List[Double](zerovec)
results.SolidPhaseMoleAmounts = List[Double](zerovec)
results.Kvalues = List[Double](Ki)
results.IterationsTaken = count
return results
udflash.PTFlash = PTFlash
PH/PS Flash
import clr
clr.AddReference('DWSIM.MathOps')
from DWSIM import *
from DWSIM.MathOps.MathEx import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.PropertyPackages import *
from DWSIM.Thermodynamics.PropertyPackages.Auxiliary.FlashAlgorithms import *
from System import *
from System.Collections.Generic import *
# gets the first Flash Algorithm (= User-Defined) added to the simulation
udflash = Flowsheet.FlowsheetOptions.FlashAlgorithms[0]
def PTFlash(Vz, P, T, pp):
n = len(Vz)
L = 0.0
V = 0.0
Vy = [0] * n
Vx = [0] * n
Ki = [0] * n
Vp = [0] * n
count = 0
alreadysolved = False
if T > Common.Max(pp.RET_VTC(), Array[Double](Vz)):
# supercritical mixture
alreadysolved = True
Vy = list(Vz)
Vx = list(Vz)
V = 1.0
L = 0.0
for i in range(n):
Vp[i] = pp.AUX_PVAPi(i, T)
Ki[i] = Vp[i] / P
Px = 0.0
for i in range(n):
if Vp[i] != 0.0: Px += Vz[i] / Vp[i]
Px = 1 / Px
Pmin = Px
Px = 0.0
for i in range(n):
Px += Vz[i] * Vp[i]
Pmax = Px
Pb = Pmax
Pd = Pmin
if Math.Abs(Pb - Pd) / Pb < 0.0000001:
# one comp only
alreadysolved = True
Px = sum(Vp * Vz)
if Px <= P:
L = 1.0
V = 0.0
Vx = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Vx[i] * Ki[i]
else:
L = 0.0
V = 1.0
Vy = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
if alreadysolved == False:
Vmin = 1.0#
Vmax = 0.0#
for i in range(n):
if (Ki[i] * Vz[i] - 1) / (Ki[i] - 1) < Vmin: Vmin = (Ki[i] * Vz[i] - 1) / (Ki[i] - 1)
if (1 - Vz[i]) / (1 - Ki[i]) > Vmax: Vmax = (1 - Vz[i]) / (1 - Ki[i])
if Vmin < 0.0: Vmin = 0.0
if Vmin == 1.0: Vmin = 0.0
if Vmax == 0.0: Vmax = 1.0
if Vmax > 1.0: Vmax = 1.0
V = (Vmin + Vmax) / 2
g = 0.0
for i in range(n):
g += Vz[i] * (Ki[i] - 1) / (V + (1 - V) * Ki[i])
if g > 0.0:
Vmin = V
else:
Vmax = V
V = Vmin + (Vmax - Vmin) / 2
L = 1.0 - V
for i in range(n):
if Vz[i] != 0.0:
Vy[i] = Vz[i] * Ki[i] / ((Ki[i] - 1) * V + 1)
if Ki[i] != 0.0:
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
else:
Vx[i] = Vz[i]
if Vy[i] < 0.0: Vy[i] = 0.0
if Vx[i] < 0.0: Vx[i] = 0.0
else:
Vy[i] = 0.0
Vx[i] = 0.0
error = 1E10
Vy_prev = [0] * n
Vx_prev = [0] * n
Ki_prev = [0] * n
V_ant = V
while error > 1E-6:
Ki_prev = list(Ki)
Ki = pp.DW_CalcKvalue(Array[Double](Vx), Array[Double](Vy), T, P)
Vy_prev = list(Vy)
Vx_prev = list(Vx)
if V == 1.0:
Vy = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
elif V == 0.0:
Vx = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Ki[i] * Vx[i]
else:
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Vz[i] * Ki[i] / ((Ki[i] - 1) * V + 1)
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
error = 0.0
for i in range(n):
error += Math.Abs(Vx[i] - Vx_prev[i]) + Math.Abs(Vy[i] - Vy_prev[i])
V_prev = V
F = 0.0
dF = 0.0
for i in range(n):
if Vz[i] > 0.0:
F += Vz[i] * (Ki[i] - 1) / (1 + V * (Ki[i] - 1))
dF -= Vz[i] * (Ki[i] - 1) ** 2 / (1 + V * (Ki[i] - 1)) ** 2
if Math.Abs(F) < 1E-6: break
V = -F / dF + V_prev
L = 1.0 - V
if V <= 0.0:
V = 0.0
L = 1.0
Vx = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vy[i] = Ki[i] * Vx[i]
if V >= 1.0:
V = 1.0
L = 0.0
Vy = list(Vz)
for i in range(n):
Vx[i] = Vy[i] / Ki[i]
if Math.Abs(V - V_prev) < 1E-6: break
count += 1
if count > 100: raise Exception("PT Flash: Maximum Iterations Reached")
print 'PT Flash iteration #' + str(count) + ' (V = ' + str(V) + ', convergence error = ' + str(error) + ')'
Vyn = [0] * n
Vxn = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
Vyn[i] = V * Vy[i]
Vxn[i] = L * Vx[i]
results = FlashCalculationResult(pp.DW_GetConstantProperties())
results.MixtureMoleAmounts = List[Double](Vz)
zerovec = pp.RET_NullVector()
results.VaporPhaseMoleAmounts = List[Double](Vyn)
results.LiquidPhase1MoleAmounts = List[Double](Vxn)
results.LiquidPhase2MoleAmounts = List[Double](zerovec)
results.SolidPhaseMoleAmounts = List[Double](zerovec)
results.Kvalues = List[Double](Ki)
results.IterationsTaken = count
return results
udflash.PTFlash = PTFlash
def Herror(Href, Vz, P, Test, pp):
tresult = PTFlash(Vz, P, Test, pp)
Vw = tresult.GetVaporPhaseMassFraction()
Lw = tresult.GetLiquidPhase1MassFraction()
Vy = tresult.GetVaporPhaseMoleFractions()
Vx = tresult.GetLiquidPhase1MoleFractions()
Hv = 0.0
Hl = 0.0
if Vw > 0.0: Hv = pp.DW_CalcEnthalpy(Array[Double](Vy), Test, P, State.Vapor)
if Lw > 0.0: Hl = pp.DW_CalcEnthalpy(Array[Double](Vx), Test, P, State.Liquid)
# calculate mixture enthalpy in kJ/kg
Hest = Vw * Hv + Lw * Hl
return (Href - Hest)
def PHFlash(Vz, P, H, Test, pp):
if Test == 0.0: Test = 273.15
T = Test
fx = 1E6
count = 0
while Math.Abs(fx) > 1E-4:
fx = Herror(H, Vz, P, T, pp)
fx2 = Herror(H, Vz, P, T + 0.1, pp)
dfdx = (fx2 - fx) / 0.1
dx = fx / dfdx
T = T - 0.7 * dx
count += 1
if count > 25: raise Exception("PH Flash: Maximum Iterations Reached")
print 'PH Flash iteration #' + str(count) + ' (T = ' + str(T) + ', current enthalpy error = ' + str(fx) + ' kJ/kg)'
result = PTFlash(Vz, P, T, pp)
result.CalculatedTemperature = T
return result
# sets the PH Flash function
udflash.PHFlash = PHFlash
def Serror(Sref, Vz, P, Test, pp):
tresult = PTFlash(Vz, P, Test, pp)
Vw = tresult.GetVaporPhaseMassFraction()
Lw = tresult.GetLiquidPhase1MassFraction()
Vy = tresult.GetVaporPhaseMoleFractions()
Vx = tresult.GetLiquidPhase1MoleFractions()
Sv = 0.0
Sl = 0.0
if Vw > 0.0: Sv = pp.DW_CalcEntropy(Array[Double](Vy), Test, P, State.Vapor)
if Lw > 0.0: Sl = pp.DW_CalcEntropy(Array[Double](Vx), Test, P, State.Liquid)
# calculate mixture entropy in kJ/[kg.K]
Sest = Vw * Sv + Lw * Sl
return (Sref - Sest)
def PSFlash(Vz, P, S, Test, pp):
if Test == 0.0: Test = 273.15
T = Test
fx = 1E6
count = 0
while Math.Abs(fx) > 1E-4:
fx = Serror(S, Vz, P, T, pp)
fx2 = Serror(S, Vz, P, T + 0.1, pp)
dfdx = (fx2 - fx) / 0.1
dx = fx / dfdx
T = T - 0.7 * dx
count += 1
if count > 25: raise Exception("PS Flash: Maximum Iterations Reached")
print 'PS Flash iteration #' + str(count) + ' (T = ' + str(T) + ', current entropy error = ' + str(fx) + ' kJ/[kg.K])'
result = PTFlash(Vz, P, T, pp)
result.CalculatedTemperature = T
return result
# sets the PS Flash function
udflash.PSFlash = PSFlash
PVF/TVF Flash
Usually you don't need to set/define a function to Pressure-VaporFraction and/or Temperature-VaporFraction Flashes unless you're working with one or more of the following:
- Phase Envelopes (Binary/Mixture)
- Centrifugal Pump (NPSH calculation)
- Force Bubble and Dew point calculation on Material Streams